Your gastrointestinal (GI) system is one of the most important aspects of your health. When you suffer from digestive issues, it can be painful — and even harmful if left untreated.
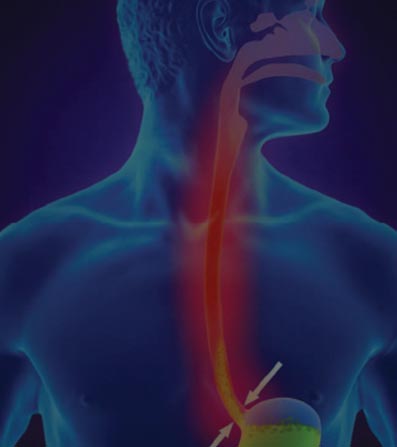
Barrett Esophagus (BE)
Barrett Esophagus (BE) is a disorder in which the lining of the esophagus (or food pipe) is damaged by stomach acid. The esophagus connects your throat to your stomach. Although cancer is not common, people with BE have an increased esophageal cancer risk.
View more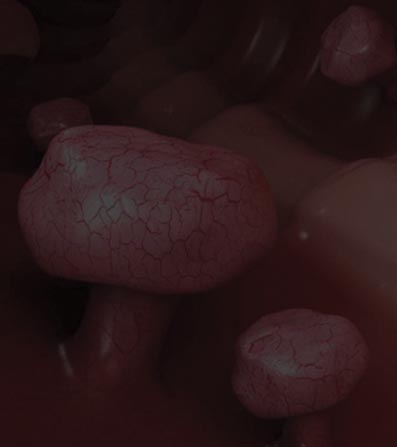
Colon Polyps
A colon polyp is a growth on the lining of the colon or rectum. Polyps of the colon and rectum are usually benign. This means they are not a cancer and do not spread. They become more common with age.
View more
Crohn Disease
Crohn Disease is where parts of the digestive tract become inflamed and usually involves the lower end of the small intestine and the beginning of the large intestine. It may also occur in any part of the digestive system from the mouth to the end of the rectum (anus). Crohn Disease is a form of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
View more
Diverticulitis
Diverticula are small, bulging sacs or pouches that form on the inner wall of the intestine. Diverticulitis occurs when these pouches become inflamed or infected. Most often, these pouches are in the large intestine (colon).
View more
Esophageal Cancer
Esophageal cancer is cancer that starts in the esophagus - the tube through which food moves from the mouth to the stomach. It is not common in the United States and occurs most often in men over 50 years old.
View more
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Gastroesophageal reflux disease occurs when the stomach contents leak backward from the stomach into the esophagus (food pipe). GERD can irritate the food pipe and cause heartburn and other symptoms.
View more
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a blood borne virus that attacks the liver. It destroys good liver cells which causes inflammation and scarring (fibrosis). If not treated, it is highly likely that cirrhosis can turn into liver cancer and require a liver transplant.
View more
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Irritable bowel syndrome is a disorder that leads to abdominal pain and bowel changes. It can occur after a bacterial infection or a parasitic infection (giardiasis) of the intestines. There are also other triggers, including stress.
View more
Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis occurs when the lining of the large intestine (colon) and rectum become inflamed. It is a form of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Crohn disease is a related condition.
View more
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a condition in which excess fat is stored in your liver. This buildup of fat is not caused by heavy alcohol use.
View more
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large gland behind the stomach, close to the first part of the small intestine, called the duodenum.
View more
Peptic Ulcer Disease
A dull or burning pain in the stomach is the most common symptom of a peptic ulcer. You may feel the pain anywhere between the belly button and breastbone.
View moreBarrett Esophagus (BE)
Barrett Esophagus (BE) is a disorder in which the lining of the esophagus (or food pipe) is damaged by stomach acid. The esophagus connects your throat to your stomach. Although cancer is not common, people with BE have an increased esophageal cancer risk.
Colon Polyps
A colorectal polyp is a growth on the lining of the colon or rectum. Polyps of the colon and rectum are usually benign. This means they are not a cancer and do not spread. They become more common with age.
Crohn Disease
Crohn Disease is where parts of the digestive tract become inflamed and usually involves the lower end of the small intestine and the beginning of the large intestine. It may also occur in any part of the digestive system from the mouth to the end of the rectum (anus). Crohn Disease is a form of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Diverticulitis
Diverticula are small, bulging sacs or pouches that form on the inner wall of the intestine. Diverticulitis occurs when these pouches become inflamed or infected. Most often, these pouches are in the large intestine (colon).
Esophageal Cancer
Esophageal cancer is cancer that starts in the esophagus – the tube through which food moves from the mouth to the stomach. It is not common in the United States and occurs most often in men over 50 years old.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Gastroesophageal reflux disease occurs when the stomach contents leak backward from the stomach into the esophagus (food pipe). GERD can irritate the food pipe and cause heartburn and other symptoms.
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a blood borne virus that attacks the liver. It destroys good liver cells which causes inflammation and scarring (fibrosis). If not treated, it is highly likely that cirrhosis can turn into liver cancer and require a liver transplant.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Irritable bowel syndrome is a disorder that leads to abdominal pain and bowel changes. It can occur after a bacterial infection or a parasitic infection (giardiasis) of the intestines. There are also other triggers, including stress.
Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis occurs when the lining of the large intestine (colon) and rectum become inflamed. It is a form of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Crohn disease is a related condition.
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a condition in which excess fat is stored in your liver. This buildup of fat is not caused by heavy alcohol use.
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large gland behind the stomach, close to the first part of the small intestine, called the duodenum.
Peptic Ulcer Disease
A dull or burning pain in the stomach is the most common symptom of a peptic ulcer. You may feel the pain anywhere between the belly button and breastbone.
